Exchange migration step by step guide
EdbMails Exchange Migration software provides a direct and reliable solution for migrating Exchange server data across on-premises Exchange, Office 365, Hosted Exchange, and other Exchange servers. It supports migrations between Exchange 2019, 2016, 2013, 2010, and 2007, including cross-forest, cross-domain, and one-hop migrations, while preserving folder structures, email properties, and permissions.
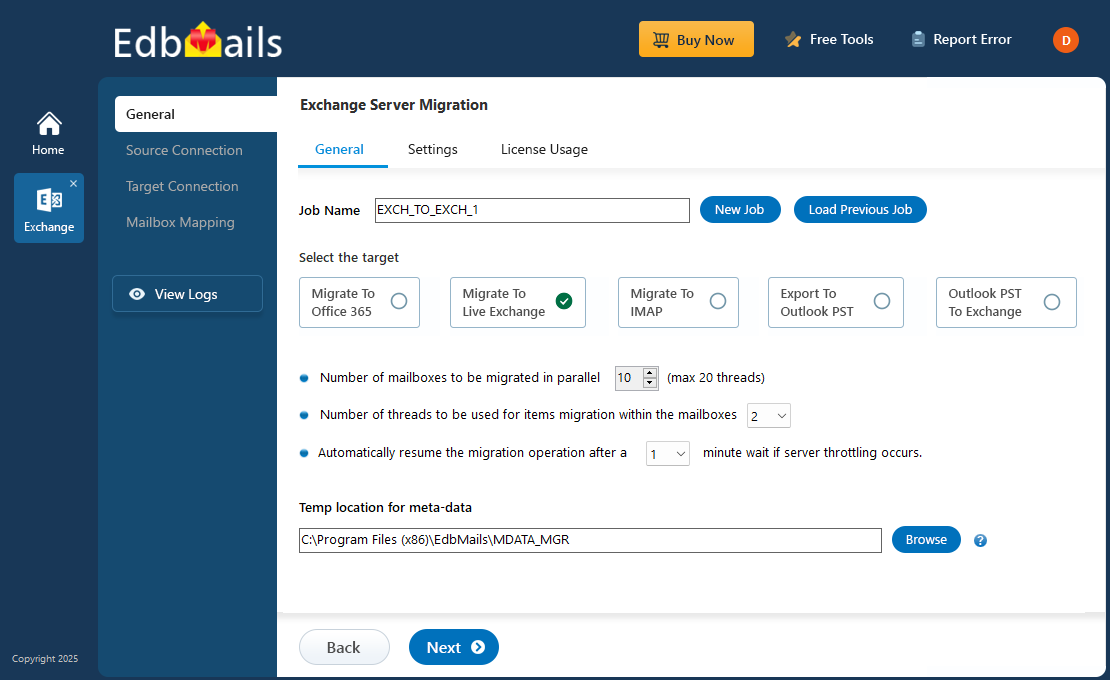
With incremental migration, EdbMails transfers only newly added or modified data, preventing duplicates and reducing bandwidth usage. The software includes automated mailbox mapping, concurrent mailbox migration, and throttling management, helping all users to migrate mailboxes, public folders, shared mailboxes, and archives while maintaining Exchange server performance.
This guide outlines the steps for pre-migration assessment, execution, and post-migration verification, assisting businesses and IT teams in managing Exchange migrations without any disruption. Whether upgrading to a newer Exchange version or migrating between Exchange servers, EdbMails ensures a structured and controlled migration process.
Exchange migration planning
Migrating Exchange server mailboxes and mail data to another server can be challenging without a proper plan. Here is a checklist of the most important factors to consider for the migration.
- Prepare a complete inventory of items that you want to migrate.
- Communicate any changes to your end users and inform the stakeholders.
- Determine the size of the mailbox data and number of mailboxes to migrate.
- Prepare the domains and required Active Directory services on the target.
- Determine if you want to migrate mailboxes along with Public folder and Shared mailboxes.
- Ensure you have enough network capacity and bandwidth to migrate.
- Consider the throttling and message size limits on Exchange server.
- Create mailboxes and Public folders on the target Exchange server
- Assign suitable licenses to the mailboxes.
- Perform a test (pilot) migration before you start the actual migration.
- Start the migration and verify the migration endpoint.
- Create new Outlook profiles and check if you are receiving mails correctly.
- Decommission the source Exchange server (optional)
Exchange migration prerequisites
- Step 1: Check that your system meets the Exchange server setup requirements
The following links will help you set up your target Exchange server. Learn more about the network, hardware, coexistence scenarios, and operating system requirements for installing Exchange.
- Exchange 2013 Server setup
- Network and directory requirement for Exchange 2016
- Network and directory requirement for Exchange 2019
- Hardware Requirements for Exchange 2016
- Hardware Requirements for Exchange 2019
- Supported operating systems for Exchange 2016
- Supported operating systems for Exchange 2019
Target Exchange server version Coexistence with the source Exchange server Requirement Migration Exchange 2019 Possible. Can coexist with Exchange 2013
Can coexist with Exchange 2016Install Cumulative Update 21 (CU21) or later on Exchange 2013
Install Cumulative Update 11 (CU11) or later on Exchange 2016With EdbMails Exchange migration software, you can migrate to any Exchange server version regardless of the coexistence issue Exchange 2016 Possible. Can coexist with Exchange 2013
Can coexist with Exchange 2010Install Cumulative Update 10 (CU10) or later on Exchange 2013
Install the latest Rollup update for Exchange 2010 Service Pack (SP3) - Step 2: Prepare your system with the following prerequisites for Exchange server
Complete the following prerequisites for Active Directory, Windows Mailbox server, and Windows Edge Transport servers before installing the target Exchange server.
- Exchange 2019 prerequisites for preparing Active Directory (AD)
- Windows Server prerequisites for Exchange 2019
- Exchange 2016 prerequisites for preparing Active Directory (AD)
- Windows Server prerequisites for Exchange 2016
Install cumulative updates (CU) on the source Exchange server For migrating Exchange on-premises to Exchange, it is required that you have the latest cumulative updates (CU) installed on the source server.
- Install for Exchange server 2013
- Install for Exchange server 2016
- Install for Exchange server 2019
Assign the Organization Management role group in Exchange to the admin user. It is an elevated permission that is required if you want to migrate Public folders.
- Step 3: Set up the target Exchange server for migration
Given below is a list of key points for installing and preparing the Exchange server for migration.
- Prepare AD and domains
- Before installing the Exchange server you need to prepare your Active Directory forest and its domains for the new version of Exchange.
- If you have a separate team to manage the Active Directory schema, you need to first extend the active directory schema, else proceed to the next step to prepare the Active Directory.
- If you have multiple domains you need to additionally prepare the Active Directory domains.
- Install Exchange server on your computer
Before installing the Exchange server, ensure that you meet the server system requirements and prerequisites as outlined previously. Next, follow the link to install Exchange 2016 or install Exchange 2019 from the setup wizard based on which server you want to migrate to.
- Prepare a clean Exchange target environment
- Create and configure a Send connector to send mail outside the Exchange organization.
- By default, Exchange automatically creates receive connectors for inbound mail flow when the mailbox server is installed. If you need to configure receive connectors, follow the steps in the link.
- Add accepted domains to allow recipients to send and receive email from another domain.
- Configure the default email address policy to add the accepted domain to every recipient in the organization.
- Configure external URLs (domains) on the virtual directories in the Client Access (frontend) services on the Mailbox server to allow clients to connect to your server from the internet (outside the organization’s network).
- Configure internal URLs on the virtual directories in the Client Access (frontend) services on the Mailbox server to allow clients to connect to your server from the internal network.
- Configure SSL certificates from a third-party certificate authority for services such as Outlook Anywhere and Exchange ActiveSync.
- Verify the Exchange server installation by running the command Get-ExchangeServer on the Exchange Management Shell (EMS)
- Create trust relationship between forests (Optional)
A forest trust is an authentication between two domains within the same Active Directory forest which creates a trust between two root domains for exchanging information. By creating a trust in advance, it is possible to address the trust issues during or after the migration.
- Create mailboxes and Public folders on the Exchange server
Before migration, it's important to ensure that mailboxes are created on the target server. EdbMails automatically creates mailboxes on the target Exchange server, streamlining the process for users. However, if you prefer to create mailboxes manually, please refer to the links below for guidance.
- Set Impersonation rights to the admin user
If you are using a global admin account to connect to the source and target Exchange servers, ensure that impersonation rights are set to the global admin user.
Steps to set impersonation rights in Exchange 2007
Steps to set impersonation rights in Exchange 2019, 2016, 2013, 2010
- Optimize EWS throttling and mail size limits for faster migration
To speed up the migration, adjust the EWS throttling settings on the target Exchange server
Steps to create custom EWS throttling policies on Exchange server
To ensure large emails are migrated, increase the message size limit on the target Exchange
Determine if you want to follow the cutover, staged or hybrid migration method.
Current environment and requirement Ideal migration approach How does the migration take place? You want to perform a complete migration to the Exchange server in a single event and in a limited time frame. Cutover migration Set up your target Exchange server and migrate everything in a single sitting. Suited for large mailbox migration You want to perform the migration in multiple phases Staged migration Migrate your mailboxes in multiple stages and transfer the most recent/required data first followed by the others. You want to migrate Exchange server data to Office 365 within the same Active directory environment Hybrid migration Migrate between Exchange and Office 365 in a hybrid environment. - Prepare AD and domains
- Step 1: Check that your system meets the Exchange server setup requirements
Exchange to Exchange Migration using EdbMails
Step 1: Download and Install EdbMails Exchange migration software
- Download and install EdbMails Exchange migration software on a Windows computer.
See a detailed list of EdbMails system requirements for Exchange migration.
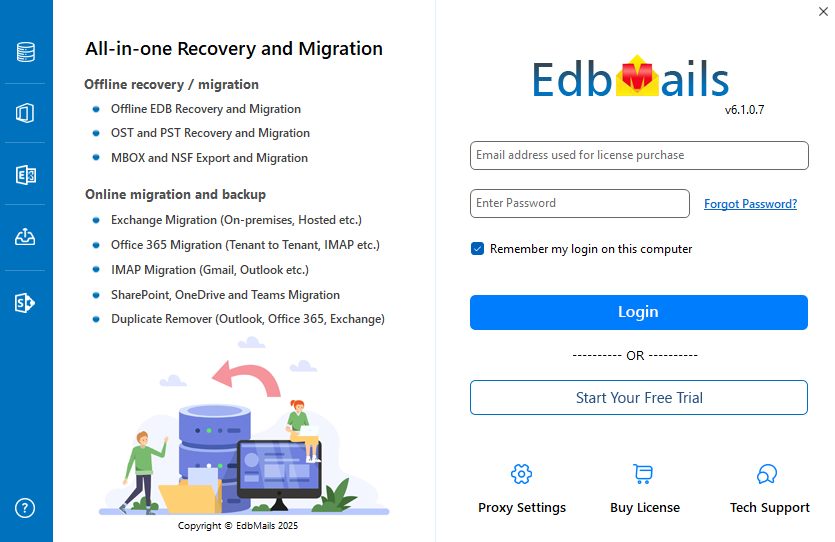
- Launch EdbMails software and Log in with your email address and password or choose ‘Start Your Free Trial’.
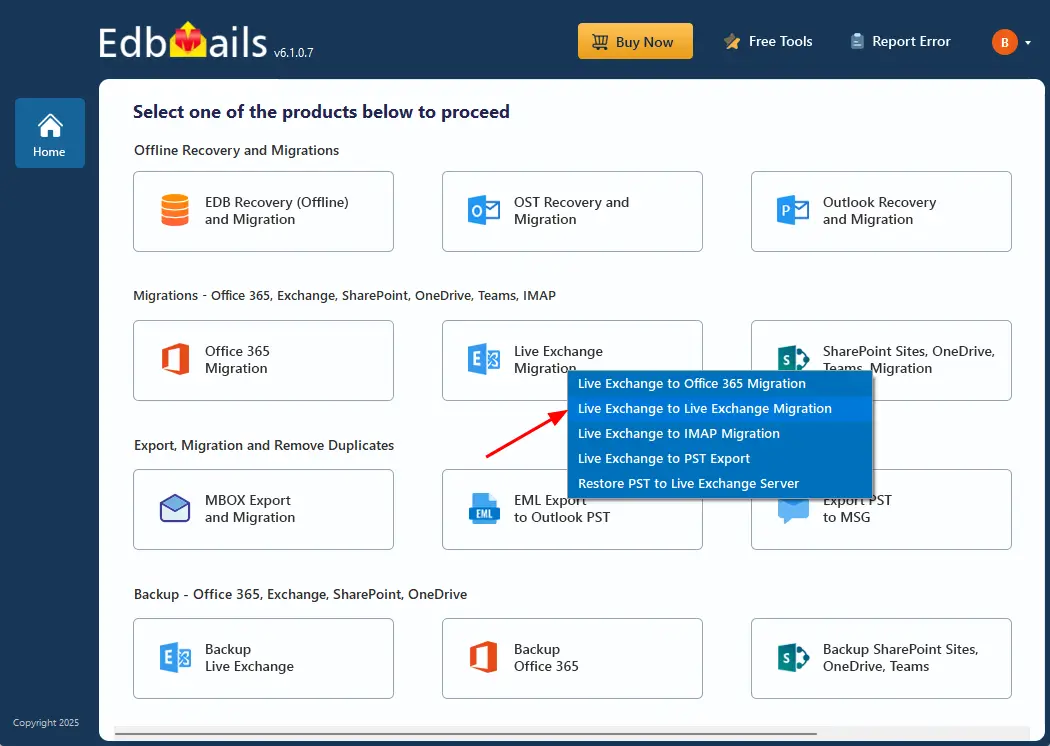
- Select ‘Live Exchange Migration’.
- Select 'Live Exchange to Live Exchange Migration'
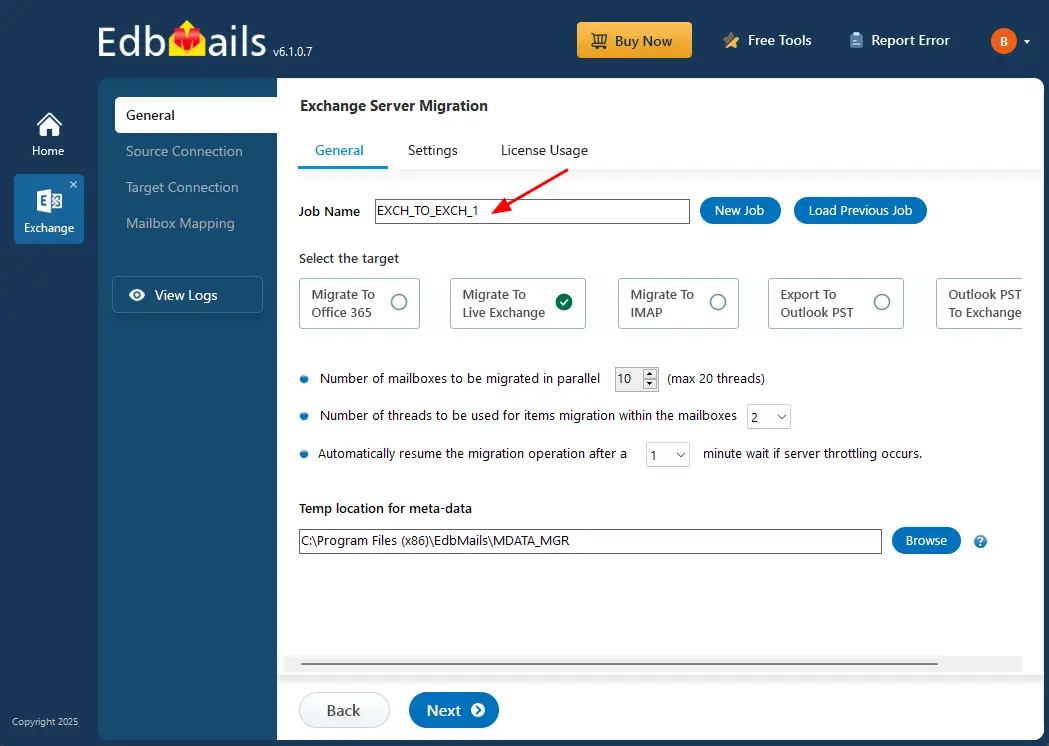
- You can either keep the default job name or click the ‘New Job’ button to change the job name.
- Download and install EdbMails Exchange migration software on a Windows computer.
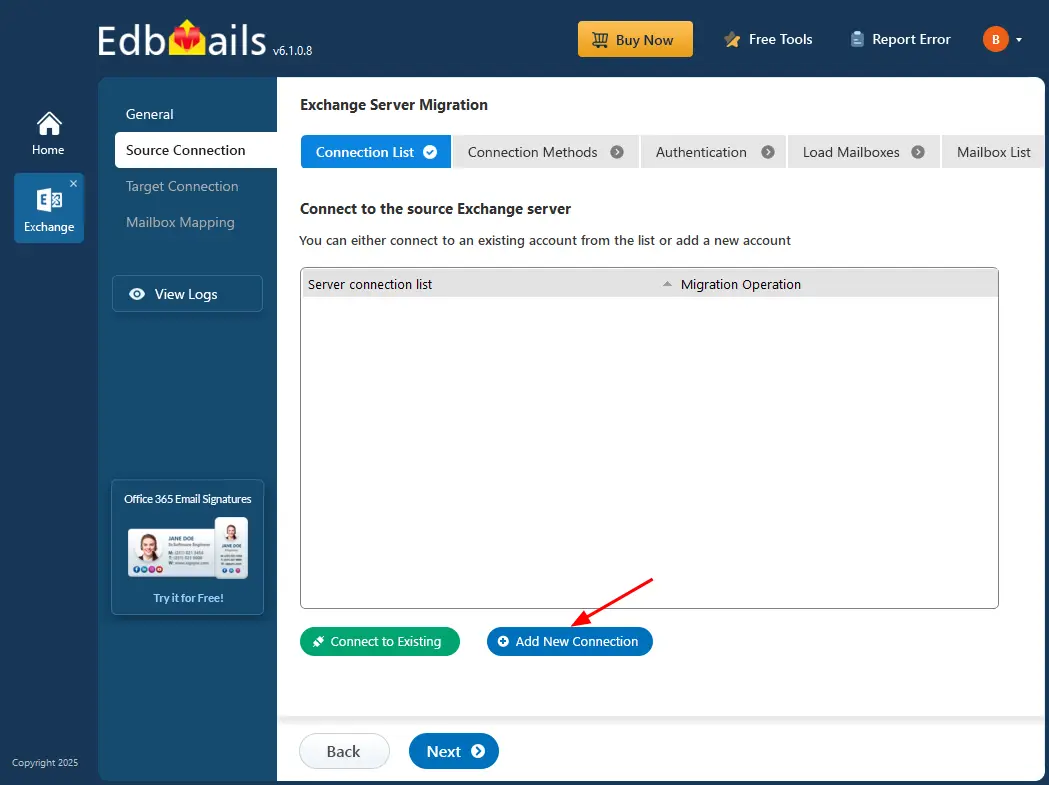
Step 2: Connect to source Exchange server
- Click the ‘Add New Connection’ button to establish a new connection to the source Exchange server. To use a previous connection, select it from the connection list and click the ‘Connect to Existing’ button to proceed.
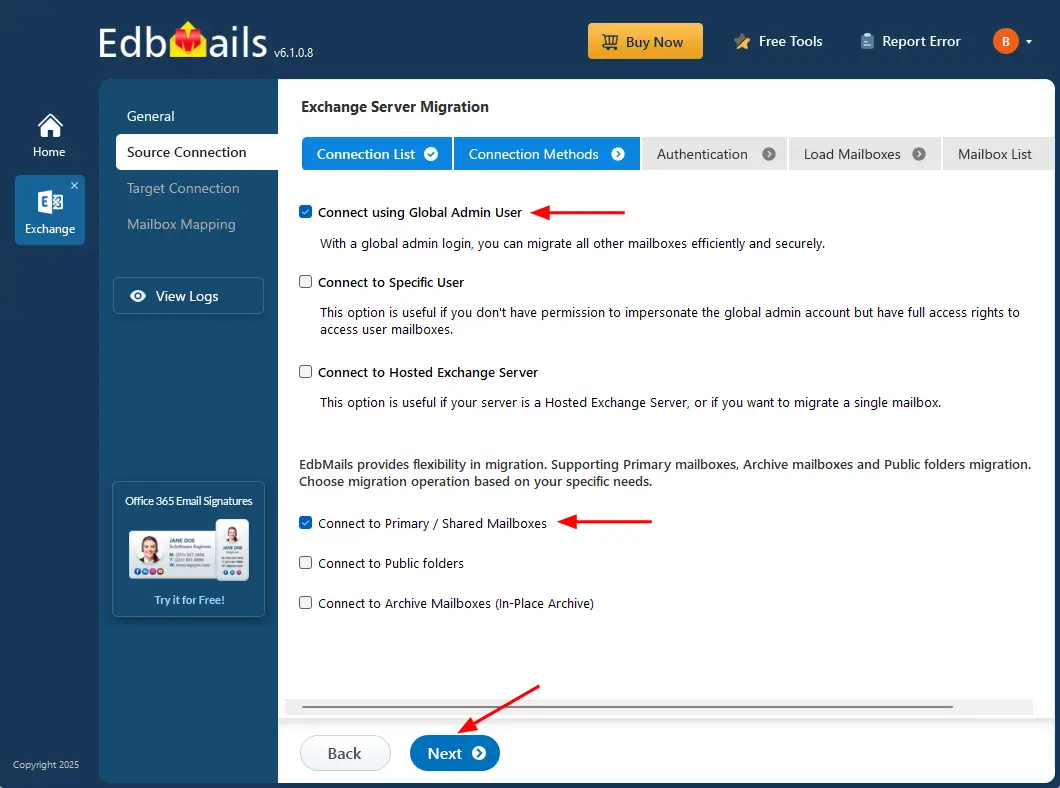
- Select the required connection options and click the ‘Next’ button.
Different options to connect to Exchange server in EdbMails
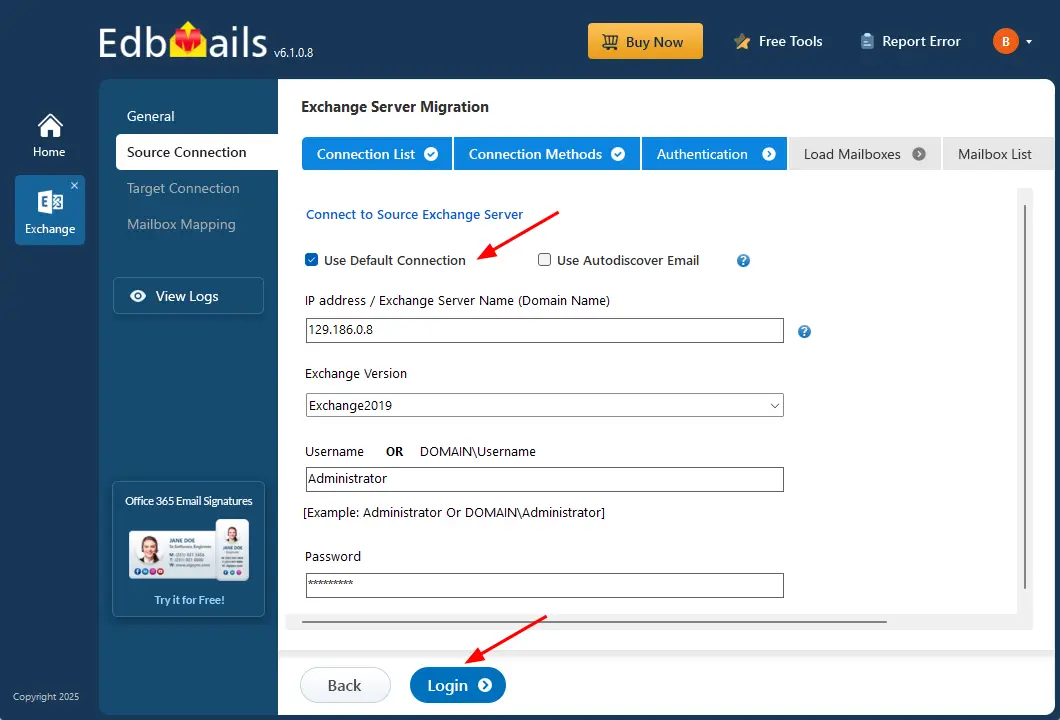
- Enter the source Exchange server details and click the ‘Login’ button
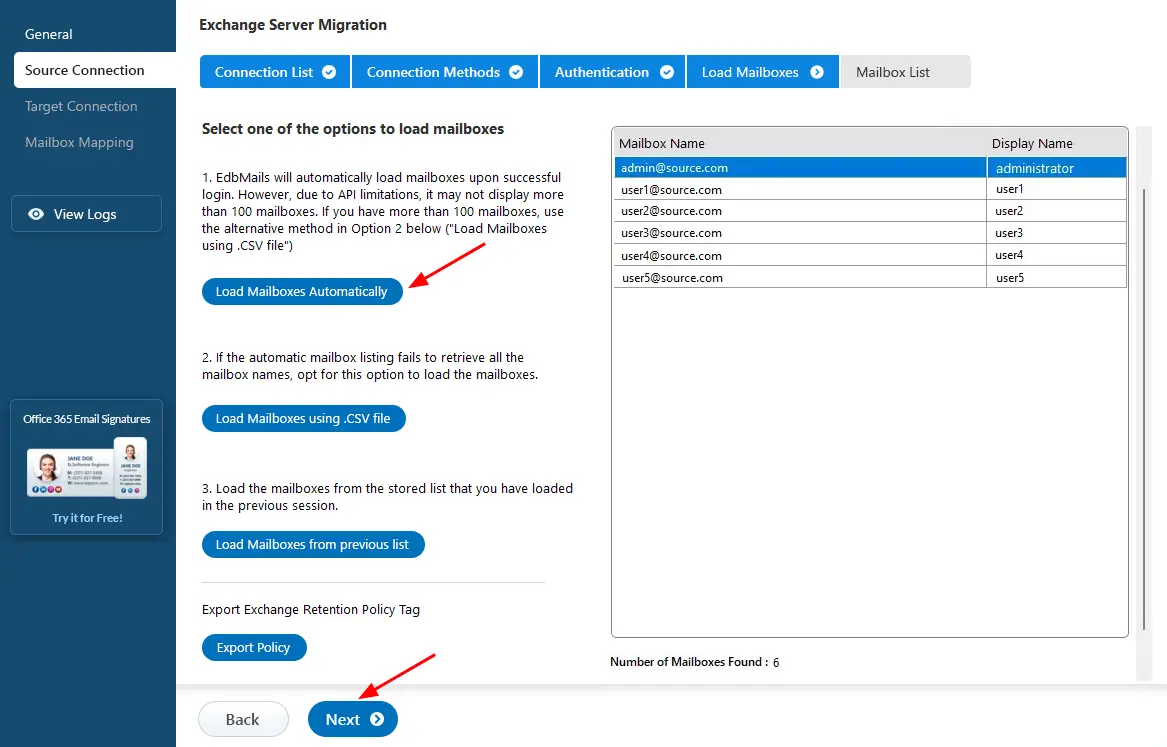
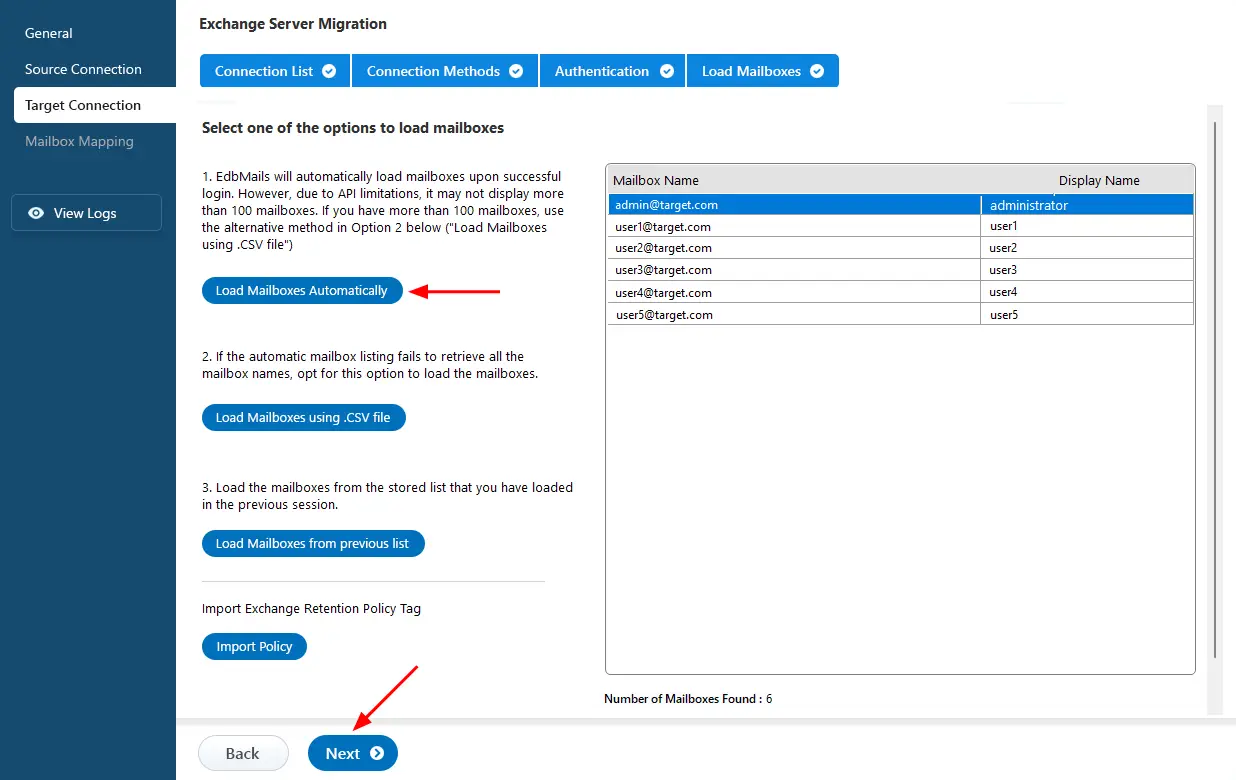
- Once you've successfully logged into your source Exchange server, select a method to load the mailboxes. EdbMails will automatically load the mailboxes, but due to Microsoft API limitations, it may not display more than 100. If you have more than 100 mailboxes, use the 'Load Mailboxes using .CSV file' option.
See how to load Exchange server mailboxes using CSV file.
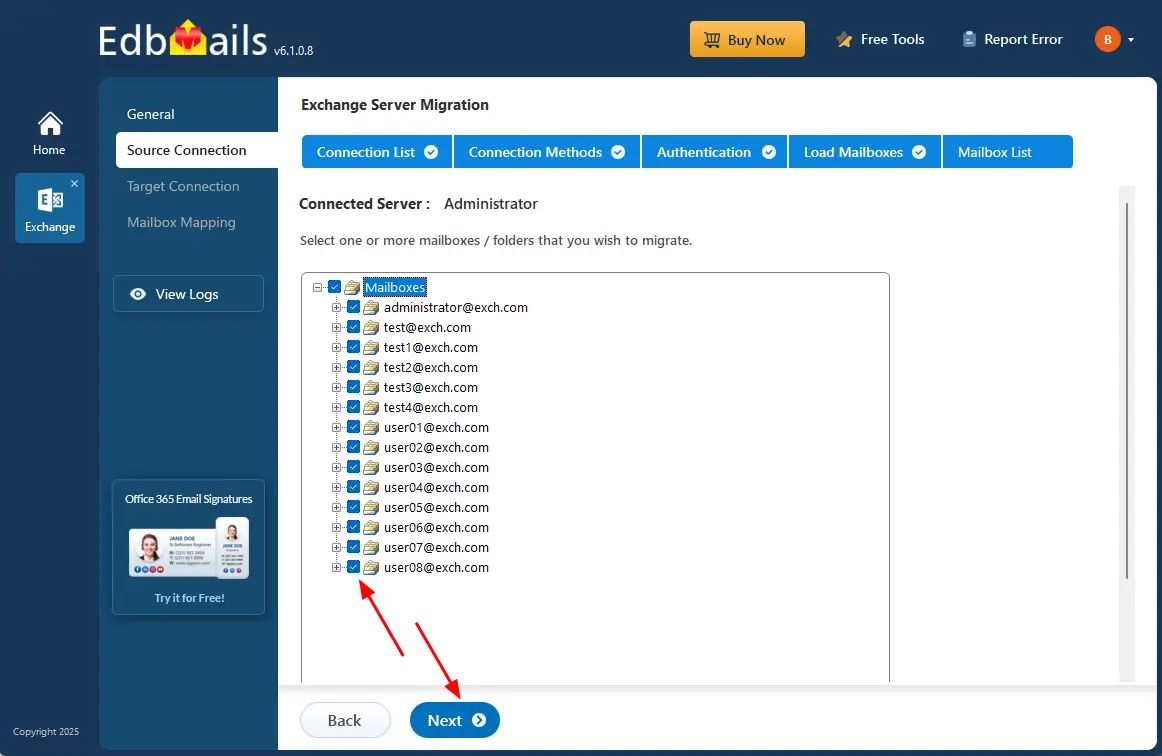
Step 3: Select the mailboxes for migration
- Select the mailboxes/folders you want to migrate from the source Exchange server.
- Click the ‘Next’ button.
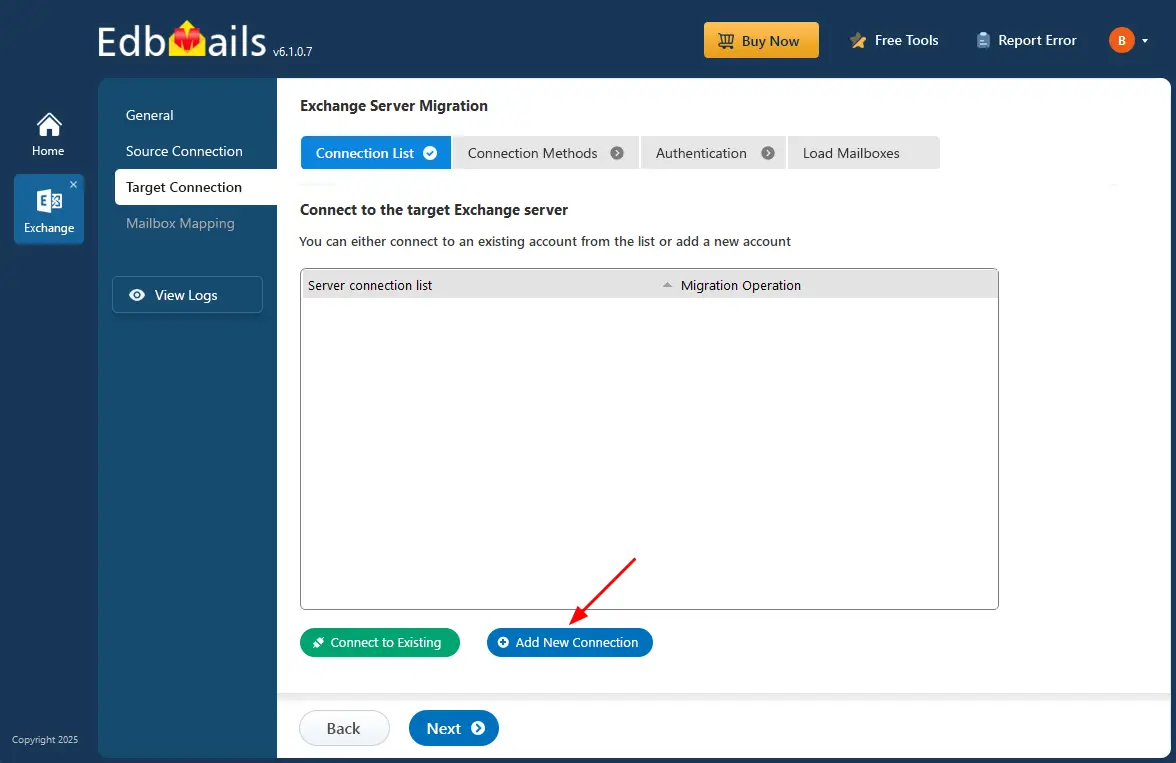
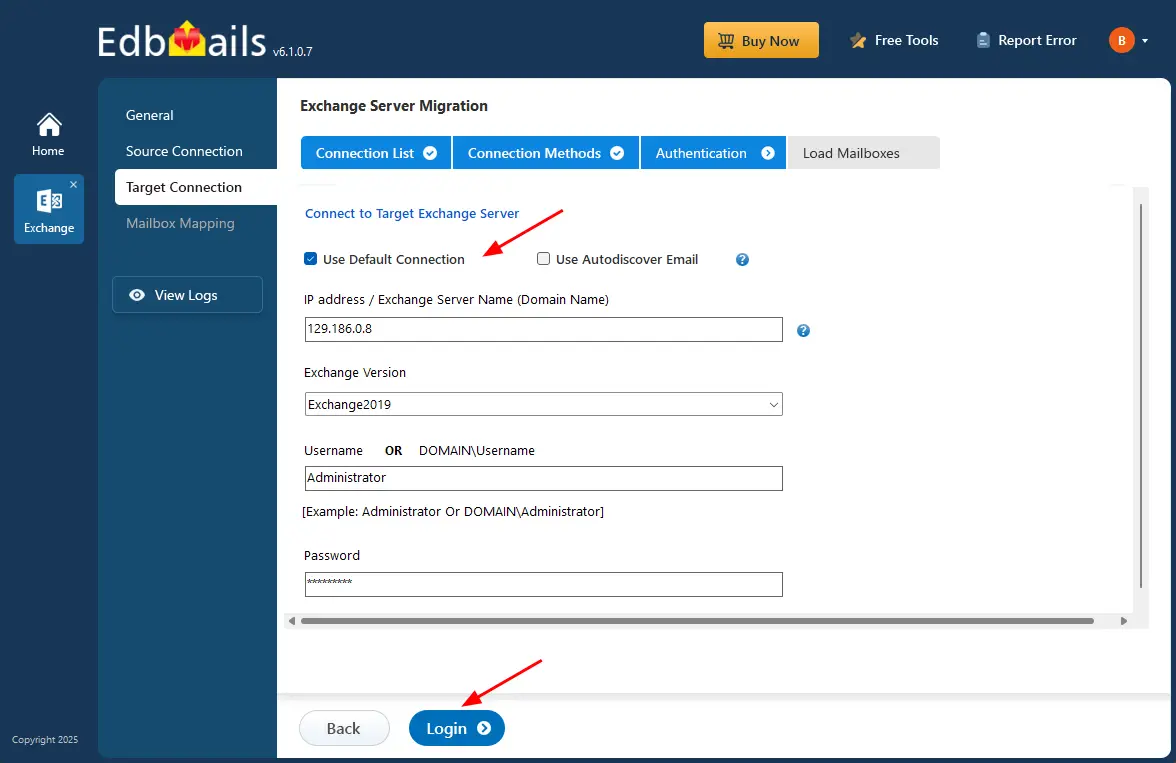
Step 4: Connect to target Exchange server
- To connect to the target Exchange server, click the ‘Add New Connection’ button to set up a new connection. If you’ve already connected before, simply choose the existing connection from the list and click ‘Connect to Existing’ to continue.
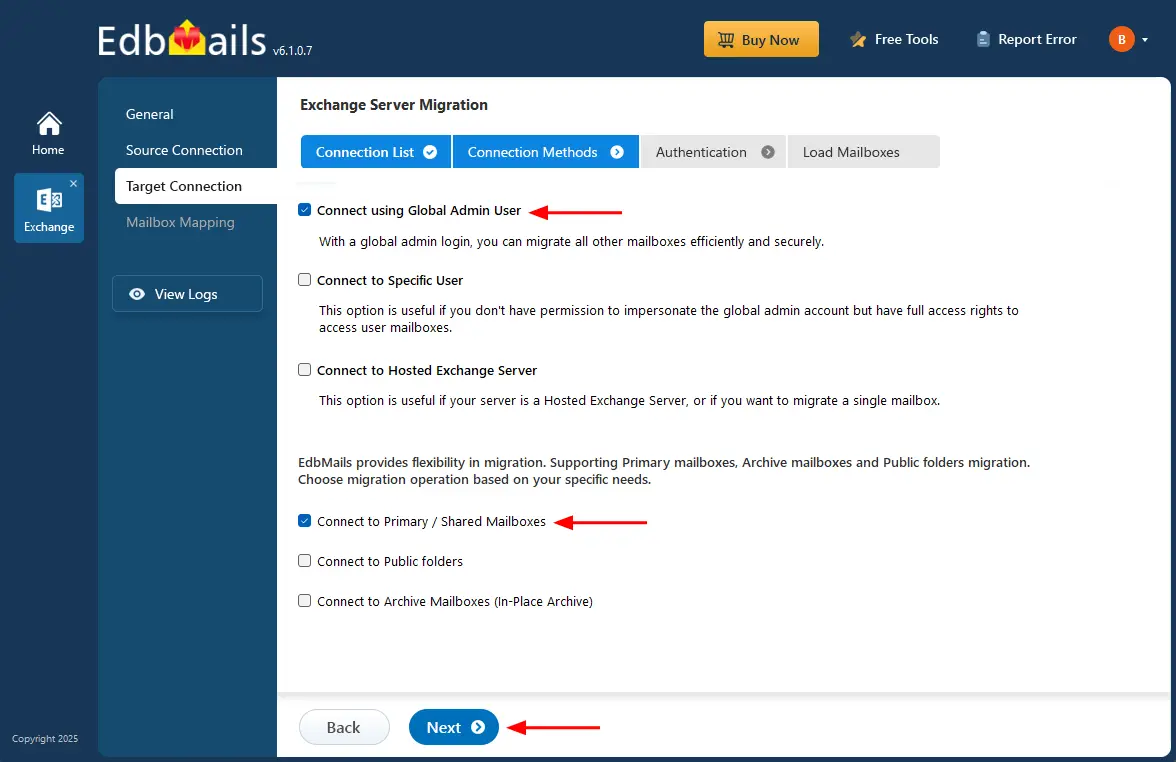
- Choose the required options to connect to your target Exchange server and click the ‘Next’ button.
- Enter the target Exchange server details and click the ‘Login’ button
- Select one of the methods to load the mailboxes.
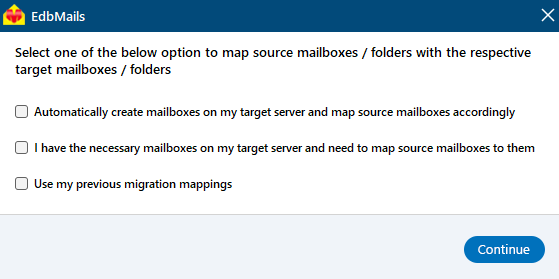
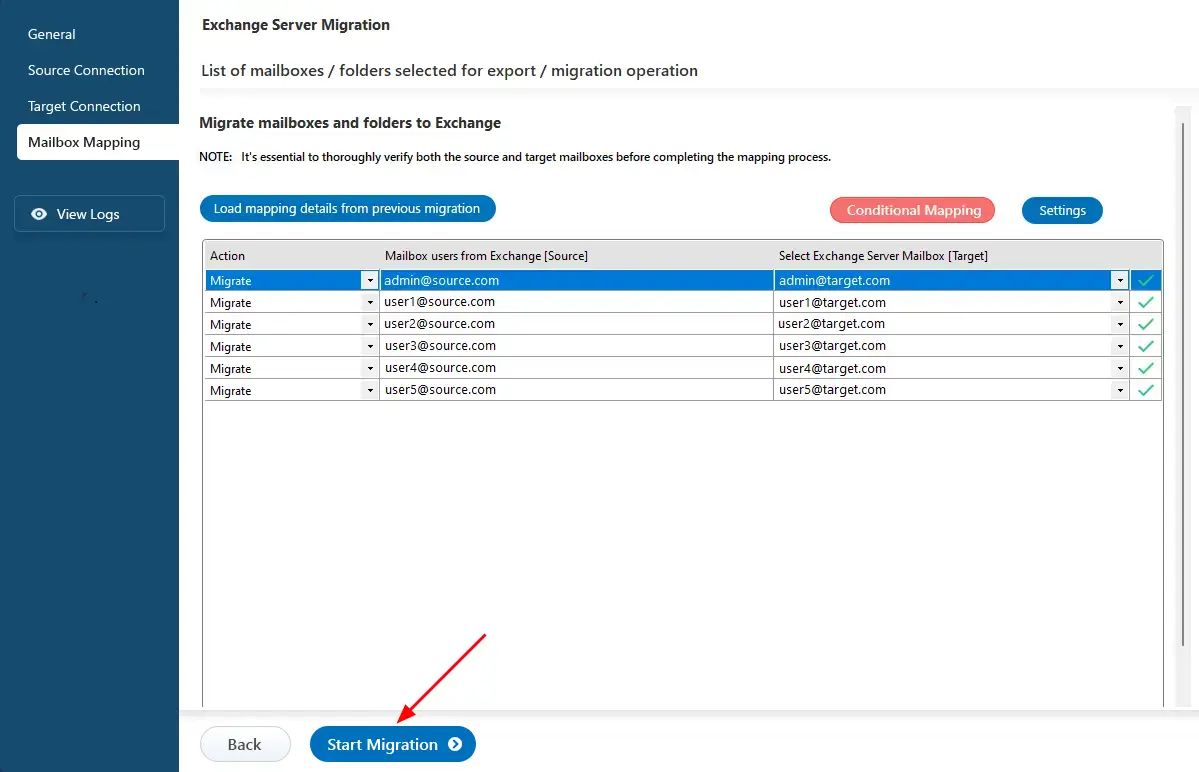
Step 5: Map source and target Exchange server mailboxes
- Select the required mapping option
- If you have installed EdbMails on your target Exchange server, you can allow EdbMails to automatically create mailboxes on the target Exchange server.
Click here to know more about automatic mailbox creation.
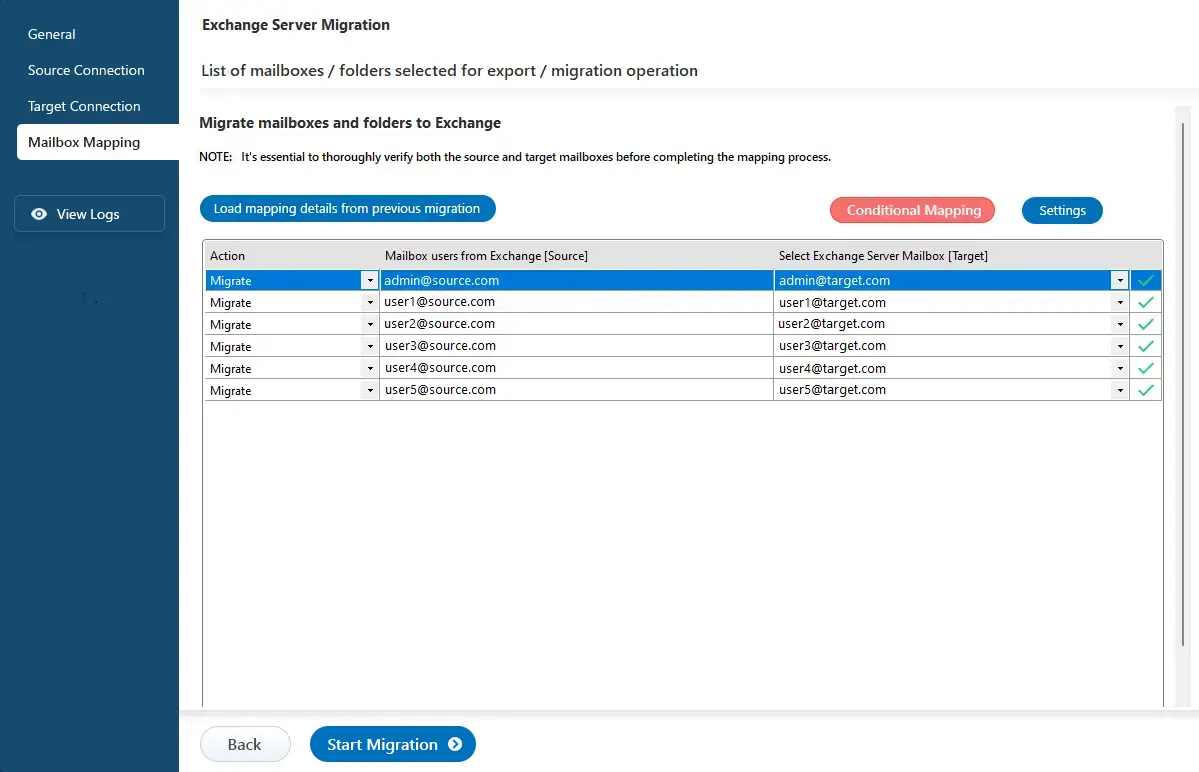
- EdbMails automatically maps mailboxes between the source and the target Exchange servers. This feature is especially useful when migrating a large number of mailboxes, as it reduces manual effort and saves time during the overall migration process.
Step 6: Start Live Exchange to Live Exchange migration operation
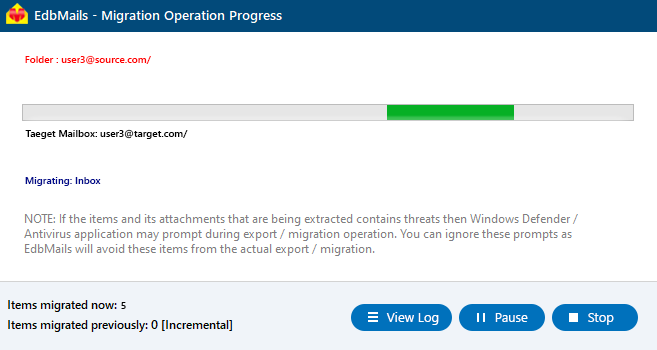
- After completing the mailbox mapping, click the ‘Start Migration’ button to initiate the migration process.
- Now that the migration has been initiated, you can see the migration status in the progress bar. Once the migration is complete, EdbMails will prompt you to review the migration status with logs.
- Click the 'View Logs' button to view the migration report. Also, log in to your target Exchange server and verify the items
Post Exchange migration activities
- Step 1: Update the MX records to point to the target Exchange server
To receive messages on the target Exchange server, update the MX records in the DNS to enable email functionality with the new server you have migrated to. In addition, configure the Autodiscover record to allow Outlook to connect to the migrated mailboxes.
- Step 2: Create a new Outlook profile for users in the new domain
Configure the Outlook profile for each user in your domain if Outlook encounters issues connecting to the new Exchange server.
- Step 3: Decommission and uninstall the source Exchange server
Uninstall and decommission the source Exchange server after you finish the migration.
- Step 1: Update the MX records to point to the target Exchange server
Exchange migration troubleshooting
See the Exchange migration troubleshooting guide for possible solutions related to migration errors. For more information on the EdbMails Exchange migration tool, see the frequently asked questions.
Advantages of using EdbMails for Exchange migration
- Granular brick-level migration of specific items.
- Incremental migration to prevent migrating duplicate items.
- Advanced include and exclude filter options for mailbox items and folders.
- Support for Exchange Public folders and shared mailbox migration.
- Data consistency with no downtime or data loss.
- Automatic mapping of mailboxes between the source and target servers.
- Direct migration from any Exchange version (2007-2019) without coexistence issues.
- Compatible with all Windows operating systems
- User-friendly interface that simplifies the migration process.
- Automatically creates target Exchange server mailboxes
- Support for concurrent mailbox migration, allowing multiple mailboxes to be migrated simultaneously for faster results.
- Automatic Office 365 throttling management to ensure optimal performance during the migration.
- Detailed migration reports for tracking the progress and results of the migration process.
- 24/7 free tech support to assist with any issues or questions during migration.